|
10 People Are Viewing This Product Right Now |
Demystifying Heat Pumps: How They Work and Why You Need One
How Does A Heat Pump Work – As temperatures fluctuate and energy costs rise, many homeowners are seeking efficient and sustainable solutions for heating and cooling their spaces. Enter heat pumps—an innovative technology that often remains shrouded in mystery despite its growing popularity. But what exactly are heat pumps, and how do they work?
This blog post aims to demystify this versatile heating and cooling system, breaking down the science behind their operation and highlighting the numerous benefits they offers. From energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints to year-round climate control, we’ll explore why investing in a heat pump could be one of the smartest decisions you make for your home.
Whether you’re considering an upgrade or simply curious about the latest in HVAC technology, join us as we unravel the secrets of heat pumps and discover how they can transform your living environment.
Introduction to Heat Pumps
 Heat pumps have emerged as a revolutionary solution in the realm of climate control, offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. Unlike conventional furnaces or air conditioners that generate heat or cool air, heat pumps transfer heat from one location to another, utilizing a clever mechanism that optimizes energy use. This process not only helps to maintain a comfortable indoor environment throughout the year but also contributes to reducing your energy bills and carbon footprint.
Heat pumps have emerged as a revolutionary solution in the realm of climate control, offering an energy-efficient alternative to traditional heating and cooling systems. Unlike conventional furnaces or air conditioners that generate heat or cool air, heat pumps transfer heat from one location to another, utilizing a clever mechanism that optimizes energy use. This process not only helps to maintain a comfortable indoor environment throughout the year but also contributes to reducing your energy bills and carbon footprint.
In essence, a heat pump operates by absorbing heat from the outside air, ground, or water—and then transferring it indoors during the colder months. Conversely, in warmer months, it reverses the process, extracting heat from your home and releasing it outside, thus keeping your living spaces cool and comfortable. This two-in-one functionality makes heat pumps an incredibly versatile choice for homeowners, capable of providing both heating and cooling solutions depending on the season.
What sets heat pumps apart is their ability to operate efficiently, even in moderate climates. They require less energy to move heat than to generate it, leading to significant energy savings throughout the year. As the world continues to shift toward more sustainable energy solutions, understanding how heat pumps work and why they are a wise investment is crucial for anyone looking to enhance their home’s energy efficiency and comfort. In this blog post, we’ll delve deeper into the mechanics of heat pumps, explore their benefits, and help you determine if this innovative technology is right for your home.
The Basics: What is a Heat Pump?
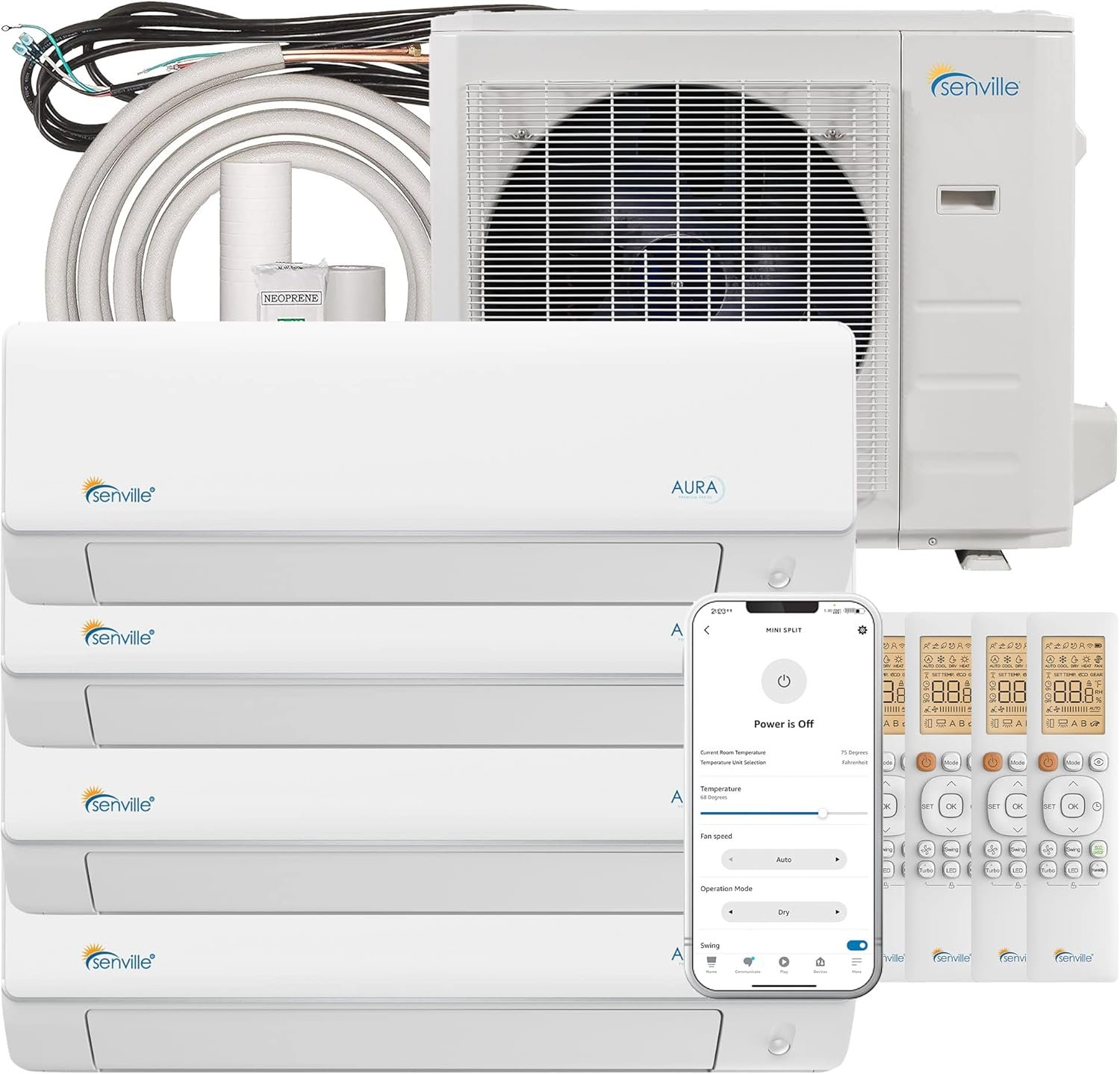
A heat pump is an innovative heating and cooling system that efficiently transfers thermal energy from one place to another, making it an essential component for modern climate control in homes and commercial spaces. At its core, a heat pump operates much like a refrigerator, but instead of removing heat from the interior to keep things cool, it can either extract heat from the outside air, ground, or water and move it indoors during colder months or vice versa in the summer.
Senville SENA
This remarkable technology utilizes a refrigeration cycle, which involves a refrigerant that absorbs and releases heat as it circulates through the system. The process begins with the refrigerant vaporizing at low temperatures as it absorbs heat from the air or ground. This vapor is then compressed, increasing its temperature and pressure before it enters the condenser coil, where it releases the absorbed heat into your living space. As the refrigerant cools, it condenses back into a liquid and returns to the evaporator to start the cycle anew.
What sets heat pumps apart from traditional heating systems, like furnaces or electric heaters, is their ability to provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile solution for year-round comfort. Moreover, heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, often producing three to four times more energy than they consume, which can lead to significant savings on energy bills. By utilizing renewable energy sources, such as the ambient heat present in the air or ground, heat pumps also reduce greenhouse gas emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice for your climate control needs. In summary, a heat pump not only keeps your home comfortable throughout the year, but it also represents a smart investment for the future of energy-efficient living.
How Heat Pumps Work: The Science Behind the System
At the heart of heat pump technology lies a fascinating interplay of thermodynamics that transforms how we think about heating and cooling our homes. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat by burning fuel or using electric resistance, heat pumps operate on a clever principle: they move heat rather than produce it.
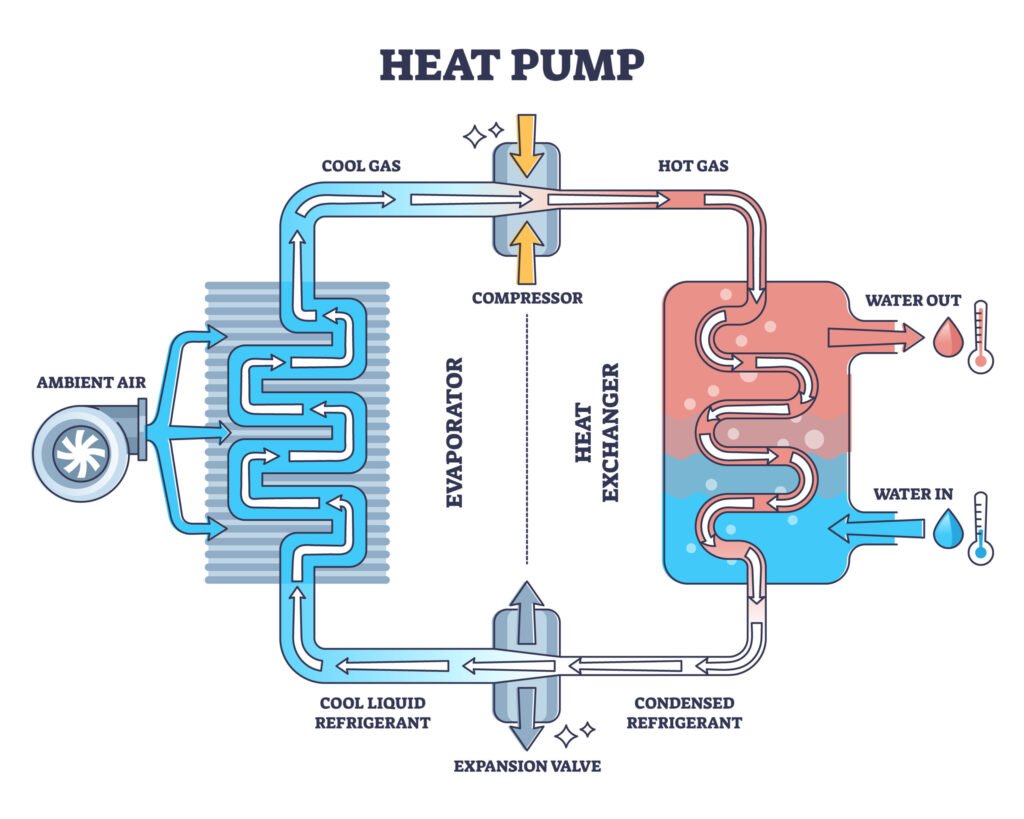
The fundamental science behind heat pumps is based on the refrigeration cycle, which involves four key components: the evaporator, the compressor, the condenser, and the expansion valve. Let’s break this down.
- Evaporator: The cycle begins in the evaporator, where a refrigerant—a fluid with a low boiling point—absorbs heat from the outside air, even in chilly temperatures. As the refrigerant absorbs this heat, it evaporates, transforming from a liquid to a gas.
- Compressor: Next, the gaseous refrigerant travels to the compressor. This component increases the pressure of the refrigerant gas, which raises its temperature significantly. The compressor is often considered the heart of the heat pump, as it is this stage that makes the heat transfer possible.
- Condenser: The high-pressure, high-temperature gas then moves to the condenser. Here, the gas releases the heat it has collected into your home’s indoor space. As the refrigerant loses heat, it condenses back into a liquid, ready to cycle back to the evaporator.
- Expansion Valve: Finally, the liquid refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, where it experiences a drop in pressure, cooling it down as it returns to the evaporator to start the process all over again.
This efficient cycle not only allows heat pumps to serve as effective heating systems in winter but also enables them to reverse the process and provide cooling in summer. By simply changing the direction of the refrigerant flow, heat pumps can draw heat from inside your home and release it outside, keeping your living spaces comfortable year-round.
The beauty of heat pumps lies in their ability to extract heat from the environment at a fraction of the energy cost of traditional heating systems. They can produce three to four units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed, making them an eco-friendly and cost-effective choice for homeowners. Understanding this science helps demystify the technology, showcasing why heat pumps are not just a trend but a smart investment for a sustainable, efficient future.
Types of Heat Pumps: Air, Ground, and Water Source
When considering a heat pump for your home, it’s essential to understand the different types available, as each operates in unique ways and suits various needs. The three primary types of heat pumps are air, ground, and water sources, each harnessing natural elements to provide efficient heating and cooling solutions.
- Air Source Heat Pumps are the most common type, utilizing the ambient air outside your home as a heat exchange medium. These pumps work by extracting heat from the outside air—even in colder temperatures—and transferring it indoors. Conversely, during warmer months, they reverse the process, removing heat from your home and releasing it outside. Air source heat pumps are relatively easy to install and can be highly efficient, making them a popular choice for homeowners looking to reduce energy costs.
- Ground Source Heat Pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, take advantage of the stable temperatures found beneath the earth’s surface. These systems require the installation of underground loops filled with a fluid that absorbs heat during the winter and releases it during the summer. While the initial installation may be more complex and costly due to the excavation required, ground source heat pumps offer exceptional energy efficiency and can provide consistent heating and cooling year-round. They are particularly beneficial in areas with extreme temperature fluctuations.
- Water Source Heat Pumps utilize bodies of water, such as lakes, rivers, or wells, as a heat exchange medium. These systems can be incredibly efficient, as water maintains a more stable temperature than air throughout the year. However, the feasibility of installing a water source heat pump depends on having access to a suitable water body and local regulations surrounding its use. These systems can be an excellent choice for properties located near sufficient water sources, offering a sustainable and efficient heating and cooling solution.
Understanding these types of heat pumps will help you make an informed decision about which system best fits your home’s needs and environmental conditions. Each type offers unique advantages, making it crucial to assess your specific requirements and consult with professionals to determine the most suitable option for your energy-efficient future.
Benefits of Using a Heat Pump for Heating and Cooling
Heat pumps are rapidly gaining popularity as an efficient and eco-friendly solution for both heating and cooling needs. One of the standout benefits of using a heat pump is its remarkable energy efficiency. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat by burning fuel or using electric resistance, heat pumps transfer heat from one place to another. During the winter months, they extract warmth from the outside air or ground and deliver it indoors, while in the summer, they reverse the process, pulling heat out of your home to keep it cool. This unique mechanism can lead to significant savings on your energy bills, as heat pumps can deliver up to three times more energy than they consume.
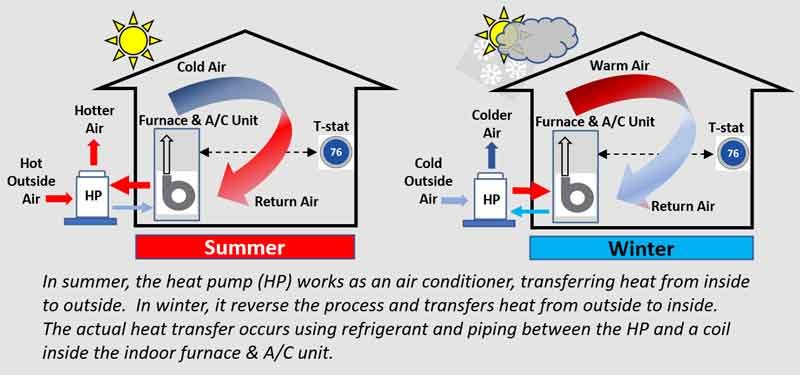
Another compelling advantage is their versatility. A single heat pump unit can provide both heating and cooling, eliminating the need for separate systems. This not only saves space but also simplifies maintenance and reduces installation costs. Moreover, many modern heat pumps come equipped with advanced features such as smart technology integration, allowing you to control the temperature of your home remotely and optimize energy use according to your schedule.
Furthermore, heat pumps are environmentally friendly. By relying on renewable energy sources, such as air or ground heat, they reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuel heating systems. For those looking to lessen their carbon footprint, investing in a heat pump is a step towards sustainable living.
Finally, heat pumps can enhance indoor air quality. Many models come with built-in filtration systems that help to remove dust, allergens, and pollutants from the air, creating a healthier living environment for you and your family. By choosing a heat pump, you’re not only investing in comfort and savings but also contributing to a cleaner planet and a healthier home.
In summary, the benefits of using a heat pump for heating and cooling are multifaceted, making it a smart choice for homeowners looking to enhance their comfort while being mindful of energy consumption and environmental impact.
Heat Pumps vs. Traditional HVAC Systems
When it comes to heating and cooling your home, the choice between a heat pump and a traditional HVAC system can feel overwhelming. Understanding the fundamental differences between these two systems can help you make an informed decision that suits your comfort needs and energy efficiency goals.
Senville SENA
Traditional HVAC systems typically rely on furnaces or air conditioners that either generate heat by burning fuel or cool air through a refrigerant cycle. In contrast, heat pumps operate on a more innovative principle: they transfer heat rather than generate it. In the winter, a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air (even when it feels cold) and transfers it indoors. Conversely, in the summer, it reverses the process, drawing heat from your home and expelling it outside, effectively cooling your living spaces.
One of the standout advantages of heat pumps is their energy efficiency. By moving heat instead of creating it, they use significantly less energy compared to traditional systems, which can translate into lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. In fact, heat pumps can deliver three to four times more energy than they consume, making them a sustainable heating and cooling solution.
Additionally, heat pumps offer versatility. Many models come equipped with features like air filtration and dehumidification, improving indoor air quality while maintaining comfortable humidity levels. This multi-functionality can simplify your home’s climate control, eliminating the need for separate heating and cooling systems.
However, it’s worth noting that performance can vary based on climate. In extremely cold regions, traditional systems may outperform heat pumps. Nonetheless, advancements in heat pump technology, such as variable-speed compressors and enhanced insulation, are making them increasingly viable in a range of climates.
In summary, while traditional HVAC systems have their place, heat pumps stand out for their efficiency, versatility, and eco-friendliness. As you weigh your options for home heating and cooling, consider how a heat pump could not only enhance your comfort but also contribute to a greener future.
Energy Efficiency: How Heat Pumps Save You Money
When it comes to energy efficiency, heat pumps emerge as champions in the realm of home heating and cooling. Unlike traditional heating systems that rely on burning fossil fuels or generating heat through electrical resistance, heat pumps operate on a fundamentally different principle: they transfer heat rather than generate it. This unique mechanism allows them to provide an impressive amount of heating or cooling for every unit of electricity consumed, often achieving efficiency ratings well over 300%.
Imagine this: on a chilly winter evening, while conventional heating systems work tirelessly to generate warmth, a heat pump quietly extracts heat from the outside air—even when temperatures dip. It then amplifies and transfers this heat indoors, creating a cozy atmosphere without the exorbitant energy bills. Conversely, during the summer months, the process is reversed. The heat pump efficiently pulls warm air from inside your home and releases it outside, keeping your living space refreshingly cool.
This dual functionality not only enhances comfort but also translates into significant savings on your energy bills. By utilizing renewable energy from the air or ground, heat pumps can reduce your reliance on traditional heating sources, leading to lower energy consumption and decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Many homeowners report savings of 30% or more on their heating bills after switching to heat pumps.
Moreover, government incentives and tax credits for energy-efficient systems can further alleviate initial installation costs, making heat pumps not only a smart choice for environmental sustainability but also a savvy financial decision. With their long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements, heat pumps represent a wise investment that pays dividends over time. In a world where energy costs are on the rise, choosing a heat pump can be a proactive step toward financial freedom while ensuring your home remains comfortable year-round.
The Environmental Impact of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps are not only a smart choice for your home’s heating and cooling needs, but they also play a significant role in reducing your environmental footprint. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely on fossil fuels and emit greenhouse gases, heat pumps operate on a fundamentally different principle: they transfer heat rather than generate it. This process dramatically lowers energy consumption and, consequently, emissions.
By drawing heat from the air or ground, heat pumps utilize renewable energy sources, making them an eco-friendly alternative. For instance, during winter months, a heat pump extracts warmth from the outside air—even in frigid conditions—and moves it indoors. Conversely, in summer, it reverses this process, providing cool air by expelling heat from your home. This dual functionality not only enhances energy efficiency but also helps in reducing reliance on air conditioning units that consume significant amounts of electricity.
Moreover, the integration of heat pumps into your home can lead to a decrease in overall energy demand. When paired with renewable energy sources like solar panels, heat pumps can operate with minimal environmental impact, effectively creating a sustainable heating and cooling system. By investing in heat pump technology, you’re not just making a smart financial decision; you’re contributing to a larger movement toward sustainability and combating climate change.
In summary, the environmental impact of heat pumps is profound. By choosing this technology, you’re taking an active role in promoting energy efficiency, reducing carbon emissions, and supporting a greener planet for future generations. Whether you’re driven by economic benefits or environmental consciousness, a heat pump is an investment that aligns with the goal of creating a sustainable and eco-friendly living environment.
Common Misconceptions About Heat Pumps
When it comes to heat pumps, misinformation can cloud understanding and deter potential users from embracing this innovative technology. Let’s take a moment to demystify some common misconceptions that may be holding you back from reaping the benefits of a heat pump system.
- Heat Pumps Don’t Work in Cold Climates
One of the most prevalent myths is that heat pumps are ineffective in colder environments. While it’s true that traditional heat pumps struggled to perform efficiently in frigid temperatures, modern advancements have led to the development of cold-climate heat pumps that are specifically designed to extract heat even when the mercury drops. These systems utilize advanced technology to maintain efficiency and comfort, ensuring that your home stays cozy all winter long. - Heat Pumps Are Only for Heating
Many people mistakenly believe that heat pumps are only useful for heating spaces. In reality, heat pumps offer year-round climate control by providing both heating and cooling capabilities. During the summer months, a heat pump can reverse its operation, effectively acting as an air conditioner and keeping your home refreshingly cool. This dual functionality makes heat pumps a versatile option for year-round comfort. - Heat Pumps Are Expensive to Operate
Another common myth is that heat pumps are costly to run. While it’s true that the initial investment may be higher than traditional heating systems, the operational costs tell a different story. Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, often consuming significantly less electricity than conventional heating systems. As a result, homeowners can expect lower utility bills, making heat pumps a cost-effective long-term solution. - Heat Pumps Require a Lot of Maintenance
Some individuals worry that heat pumps demand excessive maintenance. In reality, heat pumps require similar upkeep to conventional HVAC systems. Regular maintenance, such as filter changes and periodic check-ups, can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of the unit. With proper care, your heat pump can serve you efficiently for many years.
By addressing these misconceptions, we hope to illuminate the true potential of heat pumps and encourage more homeowners to consider this sustainable and efficient heating and cooling solution. With the right understanding, you can make an informed decision that not only enhances your comfort but also aligns with eco-friendly practices and energy savings.
Senville SENA
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Heat Pump
When it comes to selecting the right heat pump for your home, several crucial factors come into play, ensuring you make an informed decision that meets your heating and cooling needs efficiently.
- Climate: The climate in which you live is perhaps the most significant determinant in choosing a heat pump. If you reside in an area with mild winters and hot summers, a standard air-source heat pump may suffice. However, for regions with extreme temperatures, you might want to consider a cold climate heat pump, which can efficiently operate even in frigid conditions.
- Size and Capacity: The size of the heat pump, often measured in British Thermal Units (BTUs), must correspond with your home’s square footage and insulation quality. A unit that’s too small will struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures, leading to increased energy costs and wear and tear. Conversely, an oversized unit can cycle on and off too frequently, reducing efficiency and comfort. Consulting with an HVAC professional to perform a load calculation can help you select the right capacity.
- Energy Efficiency Ratings: Look for heat pumps with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings. The higher these numbers, the more efficient the unit, translating into lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint. Investing in an Energy Star-rated heat pump can also provide long-term savings and potential rebates.
- Noise Levels: Heat pumps can produce noise during operation, which may be a concern, particularly if installed near bedrooms or outdoor living spaces. Check the decibel rating of the units you’re considering and opt for models specifically designed for quieter performance, ensuring your home remains a peaceful sanctuary.
- Installation and Maintenance: The installation process can vary in complexity and cost. It’s essential to choose a reliable contractor with experience in heat pump installation. Additionally, consider the maintenance requirements of different models. Some may necessitate more frequent servicing than others, affecting your overall cost and convenience.
- Features and Technology: Modern heat pumps come equipped with various features that enhance convenience and efficiency. Smart thermostats, variable-speed compressors, and zone control capabilities can optimize your heating and cooling experience. Assess these features based on your lifestyle and preferences.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a heat pump that not only meets your heating and cooling needs but also enhances your home’s energy efficiency, comfort, and overall value. With the right choice, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying a cozy home year-round while reaping the benefits of a sustainable heating solution.
Installation Process: What to Expect
Installing a heat pump is a significant investment that can enhance your home’s comfort while lowering your energy bills. Understanding the installation process can help ease any concerns and ensure a smooth transition to this efficient heating and cooling system. Here’s what to expect:
- Consultation and Assessment: The journey begins with a thorough consultation from a qualified HVAC professional. They will assess your home’s size, insulation, and existing heating and cooling systems to determine the best type and size of heat pump for your needs. This step is crucial, as a heat pump that’s too small or too large won’t operate efficiently.
- Choosing the Right System: After the assessment, the contractor will present various options tailored to your home’s requirements. This may include discussing different types of heat pumps—air-source, ground-source, or ductless mini-splits—along with their pros and cons. You’ll also discuss energy efficiency ratings, potential rebates, and financing options.
- Pre-Installation Preparation: Once you’ve selected your heat pump, the team will prepare your home for installation. This could involve clearing the installation area, ensuring proper access to electrical systems, and even making any necessary modifications to your ductwork, if applicable.
- Installation Day: On the big day, the installation team will arrive with the required equipment and tools. The installation process can take anywhere from a few hours to a full day, depending on the complexity of the job. They’ll install the indoor and outdoor units, connect them to your home’s electrical system, and set up the necessary refrigerant lines.
- Testing and Calibration: After installation, the technicians will run tests to ensure the system operates efficiently. They’ll check for any leaks, verify proper airflow, and calibrate the thermostat for optimal performance. This step is essential to ensure your heat pump delivers the comfort you expect.
- Walkthrough and Education: Finally, the installation team will walk you through the system, explaining how it works and how to maintain it. They’ll provide tips on setting the thermostat and scheduling regular maintenance checks to ensure longevity.
By understanding the installation process, you can approach your heat pump installation with confidence, knowing you’re taking a step toward a more energy-efficient and comfortable home. With a little preparation and the right team by your side, you’ll be enjoying the benefits of your new system in no time!
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To ensure your heat pump operates at peak efficiency and longevity, regular maintenance is essential. Like any home appliance, a little care can go a long way in preventing costly repairs and maximizing performance. Here are some key maintenance tips to keep your heat pump running smoothly:
- Regular Filter Changes: One of the simplest yet most effective maintenance tasks is changing or cleaning the air filters. Clogged filters restrict airflow, forcing your heat pump to work harder than necessary. Aim to check your filters monthly, especially during peak usage seasons, and replace or clean them every 1-3 months.
- Keep the Outdoor Unit Clear: The outdoor component of your heat pump plays a crucial role in heat exchange. Ensure that it’s free from debris such as leaves, dirt, and snow. A clean unit promotes better airflow and efficiency. Trim back any shrubs or plants that might obstruct the unit and consider clearing a path for access during winter.
- Schedule Professional Inspections: Although there are many maintenance tasks you can handle on your own, it’s wise to enlist a professional for an annual inspection. A trained technician can perform a thorough check-up, including testing refrigerant levels, inspecting electrical connections, and cleaning internal components. This proactive approach can catch issues before they escalate and ensure your system is in top shape.
- Check the Thermostat Settings: Ensure that your thermostat is functioning correctly and is set to the appropriate temperature. Consider upgrading to a programmable or smart thermostat, which can optimize your heat pump’s performance by adjusting settings based on your daily schedule.
- Monitor System Performance: Pay attention to how your heat pump is performing. Are there unusual noises or fluctuations in temperature? Is it cycling on and off more frequently than normal? Any changes in performance can signal a problem that needs addressing, so don’t hesitate to consult a professional if something seems off.
- Insulate Ducts and Seals: If your heat pump system has ductwork, ensure that it is well-insulated and sealed. Leaky ducts can lead to significant energy loss, making your heat pump work harder and reducing its efficiency. Inspect the ductwork regularly and seal any gaps or leaks with duct tape or mastic sealant.
- Test the Emergency Heat Function: If your heat pump has a backup heating system (often referred to as emergency heat), periodically test it to ensure it’s operational. This feature can be a lifesaver during extreme cold spells, providing an additional layer of comfort when your heat pump is struggling.
By following these maintenance tips, you can enhance the performance of your heat pump, extend its lifespan, and ultimately save on energy costs. Regular upkeep will not only keep your home comfortable but will also give you peace of mind knowing that your heat pump is ready to tackle whatever the weather throws your way.
13. Real-Life Case Studies: Heat Pump Success Stories
When it comes to understanding the transformative power of heat pumps, real-life case studies can serve as compelling narratives that illustrate their benefits. Let’s delve into a few success stories that showcase how households and businesses have embraced this technology, reaping both economic and environmental rewards.
- Case Study 1: The Smith Family Home
In a suburb of Portland, Oregon, the Smith family was facing skyrocketing heating bills during the winter months. After conducting research, they decided to invest in a ground-source heat pump. The initial installation was a significant investment, but within a year, they noticed a dramatic reduction in their energy bills—by as much as 50%. Not only did their home maintain a consistent and comfortable temperature year-round, but the Smiths also enjoyed the added benefit of cooling in the summer. Their success story has inspired many neighbors to consider similar upgrades, showcasing how a heat pump can enhance home comfort while being financially savvy. - Case Study 2: Green Valley School District
In a bid to reduce operating costs and their carbon footprint, the Green Valley School District in Wisconsin implemented air-source heat pumps in several of their facilities. The project was part of a broader sustainability initiative. Within two years, the district reported a 30% reduction in heating and cooling expenses. Additionally, the school has become a beacon of environmental awareness, using the heat pump system as a teaching tool for students. This case highlights not only the cost savings but also the potential for heat pumps to play a role in community education and environmental stewardship. - Case Study 3: The Baker’s Bakery
A local bakery in a bustling urban center opted for a heat pump system to address their heating and cooling needs, especially during peak baking seasons. By switching to a high-efficiency heat pump, they were able to maintain optimal temperatures for their ovens while creating a comfortable atmosphere for customers. The bakery saw a 40% decrease in energy costs and reported an increase in customer satisfaction—thanks in part to the stable indoor climate. Their story illustrates how heat pumps can drive efficiency and create a pleasant environment for both employees and patrons.
These case studies provide tangible evidence that heat pumps are not just a theoretical solution; they are a practical choice that can lead to significant savings and increased comfort. Whether in a family home, a school district, or a small business, the success stories underscore the versatility and effectiveness of heat pumps in real-world applications. As you consider the advantages of this innovative technology, let these examples inspire you to take the next step toward energy efficiency and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Pumps
As interest in sustainable and energy-efficient solutions continues to rise, many homeowners are turning to heat pumps as a viable option for heating and cooling their spaces. However, with this growing popularity comes a myriad of questions. To help clarify common concerns and shed light on the functionality of heat pumps, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions that address the most pressing inquiries.
- What exactly is a heat pump?
A heat pump is a versatile system that transfers heat from one place to another, providing both heating and cooling functionalities. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, heat pumps move existing heat from the air, ground, or water. This makes them highly efficient, as they can deliver up to three times more energy in heating or cooling than they consume. - How do heat pumps work in winter?
During the colder months, heat pumps extract heat from the outside air (even when it’s cold) and transfer it indoors, keeping your home warm and comfortable. They utilize a refrigerant that absorbs heat from the outside air, compresses it, and then releases it indoors. Thanks to advancements in technology, modern heat pumps can operate efficiently even in frigid temperatures. - Are heat pumps energy-efficient?
Absolutely! Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency and can significantly reduce energy bills. They provide a higher coefficient of performance (COP) compared to conventional heating systems, meaning they deliver more energy than they consume. In fact, many heat pumps can reduce energy use for heating by 50% compared to traditional electric resistance heating. - Do heat pumps require a lot of maintenance?
While heat pumps do require regular maintenance to operate efficiently, they are generally less demanding than conventional heating systems. Regular checks, such as cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting ducts, and ensuring there’s no obstruction around the outdoor unit, can keep your heat pump running smoothly for years to come. - What about the upfront costs?
The initial investment for a heat pump can be higher than traditional heating systems. However, considering the long-term savings on energy bills and potential tax incentives for energy-efficient home improvements, many homeowners find that heat pumps offer a cost-effective solution over time. - Can heat pumps work in every climate?
Heat pumps are versatile and can be effective in various climates. While air-source heat pumps are best suited for moderate climates, ground-source (or geothermal) heat pumps can provide efficient heating and cooling in nearly any environment. It’s essential to assess your local climate and choose the appropriate type of heat pump for your needs.
By addressing these common questions, we hope to demystify heat pumps and highlight their benefits. As more homeowners consider eco-friendly alternatives, understanding how heat pumps work and their advantages can empower you to make informed decisions for your home’s heating and cooling needs. Whether you’re looking to reduce your carbon footprint, cut energy costs, or simply improve your home’s comfort, a heat pump may be the ideal solution for you.
Senville SENA
Conclusion: Why You Should Consider a Heat Pump for Your Home
In conclusion, embracing the efficiency and versatility of heat pumps can profoundly transform your home’s energy dynamics. As we’ve explored throughout this blog, heat pumps offer a sustainable solution for both heating and cooling, making them an exceptional choice for year-round comfort. With their ability to transfer heat rather than generate it, they utilize significantly less energy compared to traditional heating systems, leading to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Moreover, advancements in technology have made modern heat pumps more reliable and efficient than ever. They are capable of operating effectively in various climates, ensuring that your home remains cozy during the winter chill and refreshingly cool in the summer heat. The installation of a heat pump not only enhances your home’s energy efficiency but can also increase its value, making it a smart investment for current and future homeowners.
Furthermore, with various models available, including air-source, ground-source, and ductless systems, there is a heat pump solution to suit nearly every home and lifestyle. By investing in a heat pump, you are choosing a system that aligns with the growing demand for energy-efficient, environmentally friendly alternatives.
As you consider your options for home heating and cooling, think of the long-term benefits that a heat pump can offer. From substantial savings on energy costs to contributing to a more sustainable future, the advantages are clear. If you’re ready to enhance your home’s comfort while being kind to the planet, it’s time to make the leap and consider a heat pump as your next home upgrade.













